What is an internship?
Internships are immersive learning experiences that offer individuals, typically students or recent graduate students, the chance to apply their academic knowledge in a real-world setting.
This means that interns work within an organization for a fixed period, usually ranging from a few weeks to several months, gaining hands-on experience in their chosen field.
In the dynamic landscape of professional development, internships, and fellowships are two terms often used concurrently. Although both programs provide valuable opportunities for individuals to gain real-world experience, there are distinct differences between internship and fellowship.
Why Internship is a Gateway to the Professional World
For high school students and recent graduates, internships are an essential means of bridging the knowledge gap between academia and real-world experience. Their main goal is to provide people a firsthand insight into the working world so they may apply abstract ideas to practical situations.
Internships facilitate the development of skills and provide possibilities for networking through practical duties. The duration varies from a few weeks to multiple months. Improved employability, a more defined career path, and insightful knowledge of industrial dynamics are among the results, equipping participants for the demands of the workplace.
Key Features of Internships
Internships are generally aimed at learning and skill development. Interns are expected to contribute to daily tasks while also receiving supervision and assistance.
Internships are brief, allowing participants to explore many aspects of a job without making a long-term commitment. This brevity allows for diversified exposure and research in a short period, resulting in academic credit.
Internships offer varying remuneration. Some pay, while others are unpaid or provide hourly earnings. The primary advantage, however, is the crucial learning experience obtained, which prioritizes skill development over money compensation.
Internships are typically entry-level positions that provide individuals with their first opportunity to work in a certain industry or firm. This introductory experience promotes professional exposure and builds the groundwork for future careers.
What are Fellowships?
Fellowships are more advanced, specialized programs that target postgraduate students with some professional experience. Fellowships are designed to cultivate leaders, researchers, or experts in a specific field and may include a structured curriculum.
What Characterizes a Fellowship Program?
Typically, fellowships are longer than internships, lasting anything from a few months to several years. A person may receive a distinguished fellowship that lasts for a substantial amount of their career.
A substantial emphasis on specific research, leadership development, or specialized training is necessary for fellowships. Fellowships require that the participants make a significant contribution to their field following the fellowship period.
Unlike many internships, many fellowships give financial support, often in the form of a stipend or hourly wages. Participants like emerging leaders can concentrate on their work without having to worry about money as a result of this.
Fellowships are intended for people who have more in-depth knowledge of their profession. They offer chances for networking, teamwork, and maybe even the start of ground-breaking projects.
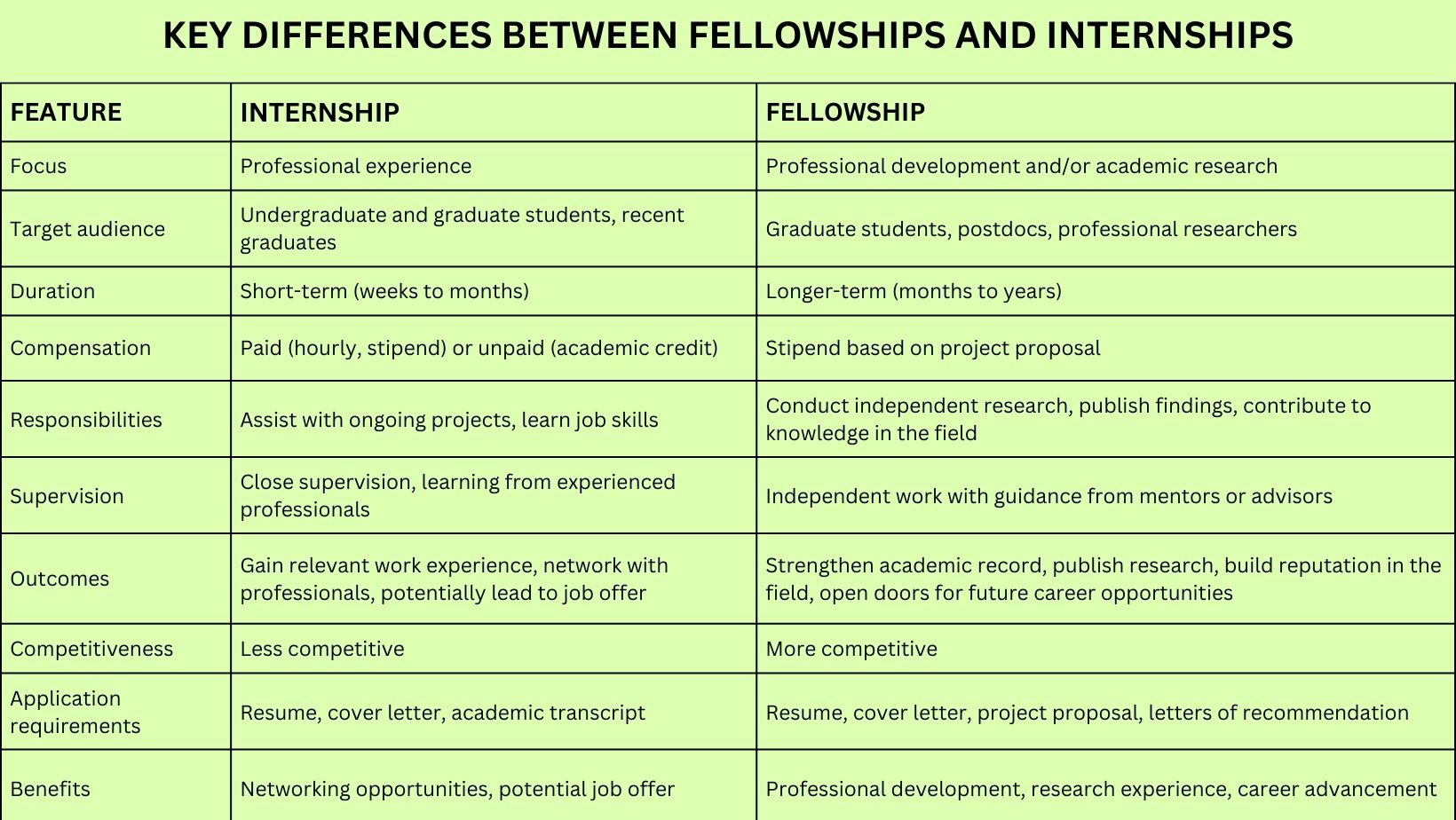
What are the Key Differences between Internships and Fellowships?
While internships and fellowships provide great learning opportunities, their objectives and target audiences differ significantly.
Internships are designed to provide practical experience in a professional setting. Fellowships, on the other hand, emphasize academic and research advancement and are frequently awarded to graduate students and researchers.
Internships are mostly aimed at undergraduates and recent graduates and last for shorter periods (weeks to months), to aid with ongoing initiatives. Fellowships on the other hand, last longer (months to years) and require independent study, which typically results in published conclusions.
Internships are hourly, project-based, or academic credit compensation options are all available. Fellows, however, are compensated based on their research projects. While both are very competitive, fellowships typically need more detailed applications, such as project proposals and letters of recommendation.
Internships are frequently sponsored by businesses and organizations, whereas fellowships are usually funded by universities, research institutions, or government bodies.
Internships may be mandatory for academic programs, whereas fellowships are typically voluntary extracurricular options.
Internships can lead to full-time employment, whereas fellowships frequently prepare candidates for further academic or research positions.
How do you choose Between Internships and Fellowships?
When deciding between internships and fellowships, it's crucial to consider your current career stage, goals, and the level of commitment you're willing to make.
Internships are excellent for those seeking entry-level experiences and exploring different industries, while most fellowships are more suitable for individuals with a clear career path, looking to specialize and make a significant impact in their chosen field.
Eligibility between internships and fellowship
Internships are typically available to current students providing them with practical experience in their study. Some internships also welcome entry-level professionals seeking to explore new industries. In contrast, fellowships target advanced degree holders, mid-career professionals, and industry experts. These programs aim to foster specialized skills, leadership, and research initiatives.
Although internships cater to early-career individuals, fellowships attract those with advanced expertise, contributing to their respective fields through impactful projects, research, and leadership development. Specific criteria vary by program and industry.
The industrial perspective between Fellowship vs Internship
Industries vary in their appreciation for internships and fellowships, with each playing a distinct role in workforce development. Tech and creative sectors often highly value internships, seeing them as crucial pipelines for fresh talent.
In contrast, research-intensive fields, such as science or academia, prioritize fellowships, recognizing their role in cultivating specialized expertise. Insights from professionals across sectors reveal that internships foster adaptability and diverse skill sets, while fellowships contribute to innovation and advanced problem-solving.
This industry perspective emphasizes the nuanced significance of both programs in shaping a skilled and versatile workforce capable of meeting diverse sectoral demands.
Expectations from the candidate
Candidates should show genuine interest in the field, industry, or organization. They should communicate a clear understanding of the program's objectives and how it aligns with your career goals.
They should demonstrate flexibility and adaptability to different tasks and work environments. As a candidate, you need to showcase an ability to learn quickly and apply new knowledge effectively.
Candidates should be open to feedback and actively seek opportunities for personal and professional growth. They should take advantage of mentorship and networking opportunities provided by the program.
Tips and Tricks for Applying the Internships and Fellowship
Navigating the application process for internships and fellowships requires strategic approaches. Crafting a compelling cover letter is essential for internship seekers, emphasizing relevant skills and experiences.
For many fellowships, standing out in the competitive selection process involves showcasing a clear alignment between personal goals and the program's objectives. Tailoring application materials, highlighting achievements, and demonstrating a genuine passion for the industry are universal tips.
Networking, informational interviews, and researching the organization's values also enhance the chances of success. This guidance ensures that individuals effectively communicate their qualifications and aspirations, increasing their competitiveness in the pursuit of valuable professional opportunities.
Trends in Internships and Fellowships
The integration of technology is reshaping these opportunities, with virtual internships becoming more prevalent, providing flexibility and access to a global talent pool. Remote work trends have influenced how internships and fellowships operate, enabling collaboration across geographical boundaries.
The future will likely see a continued shift towards tech-driven, remote-friendly experiences, fostering a more inclusive and interconnected approach to professional development in the ever-changing global workforce.
Impact on Resume
Internship and fellowship programs elevate a resume, signaling practical experience and dedication. Internships demonstrate hands-on industry exposure, while academic fellowships indicate specialized training and a commitment to excellence. Employers value these experiences, as they showcase a candidate's adaptability, skills acquisition, and a proactive approach to professional development, contributing significantly to a well-rounded and competitive professional profile.
Which one is better between internship and fellowship?
The choice between an internship program and fellowship depends on individual career goals and experience. Internships are ideal for early-career individuals exploring industries, offering practical exposure and skill development. Fellowships suit seasoned professionals or those with a bachelor’s degree, providing specialized training and leadership opportunities. Both have unique merits, with internships serving as stepping stones and fellowships elevating careers through focused expertise and impactful contributions.
Challenges and Consideration
Fellowships and internships present difficulties, such as intense competition for few spots, which raises questions regarding equitable access. Unpaid or inadequately compensated jobs raise the possibility of exploitation and affect people's financial security.
Insufficient availability complicates the problem even more, creating obstacles for eligible applicants to overcome. Finding the right mix to guarantee equitable opportunities, appropriate pay, and greater accessibility is still crucial while navigating various career development routes.
Success Stories from Internships and Fellowships
Real-world success stories highlight the transformative power of internships and fellowships. Mark Zuckerberg, Facebook's co-founder, started his career as an intern at a software company, refining his coding talents and eventually revolutionizing social media.
Colonel Harland Sanders, the famed founder of KFC, used a fellowship from the Kentucky Colonel title to launch a storied career in the food sector. These stories demonstrate the transformative power of strategic career development through actual experiences.
To Wrap Up
Internships and fellowships cater to different stages of a person's career although they offer valuable opportunities for professional growth. Internships provide a taste of the professional world, allowing individuals to develop foundational skills, whereas fellowships are advanced programs designed to foster expertise and leadership. By understanding these key differences, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your career goals and aspirations.







